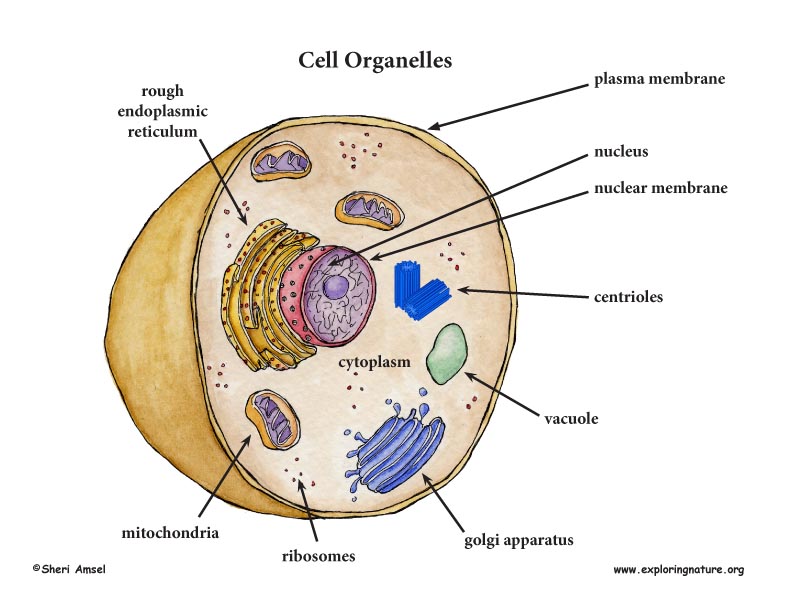
Each cell has a protective outside layer called the plasma membrane. The plasma membrane lets certain things into the cell that it needs, but keeps other things out. This is called semipermeable. Inside the cell is a watery medium that everything floats in called cytoplasm. The cytoplasm contains all the working parts of the cell, the organelles. Each organelle has a job. The nucleus has our DNA that contains all our genetic information. The DNA is found on structures in the nucleus called chromosomes. There are 23 pairs (46 total) of chromosomes in each nucleus of each cell. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane, which controls what goes in and out. Little grains floating around inside the cell are ribosomes, where proteins are made. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) is a bunch of folded membrane pathways spotted with ribosomes. Together the ribosomes and the rough ER make new proteins and new membranes that the cell needs. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (smooth ER) has no ribosomes on it and makes containers called vesicles that are used to move things around inside the cell. Golgi apparatus are made up of flat vesicles that package up things that need to leave the cell, like hormones. Lysosomes are vesicles that have digestive enzymes inside them and break down the things that the cell doesn't need. They also kill bacteria that invades the body. Vacuoles are membrane sacs for storing things. Mitochondria have a double membrane that folds in on itself forming little fingers called cristae. They break down sugar to make ATP, which is used by the cell as energy. All the organelles are working together to keep things in the body in balance (equilibrium).
Plants are made up of cells too. Plant cells are a bit different from animal cells. For one thing, plant cells have a thick cell wall surrounding the plasma membrane. Their vacuoles, which store water, are much larger. They have chloroplasts, the organelles that carry out photosynthesis, to make energy for the plant using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide.
Cell Organelle Facts:
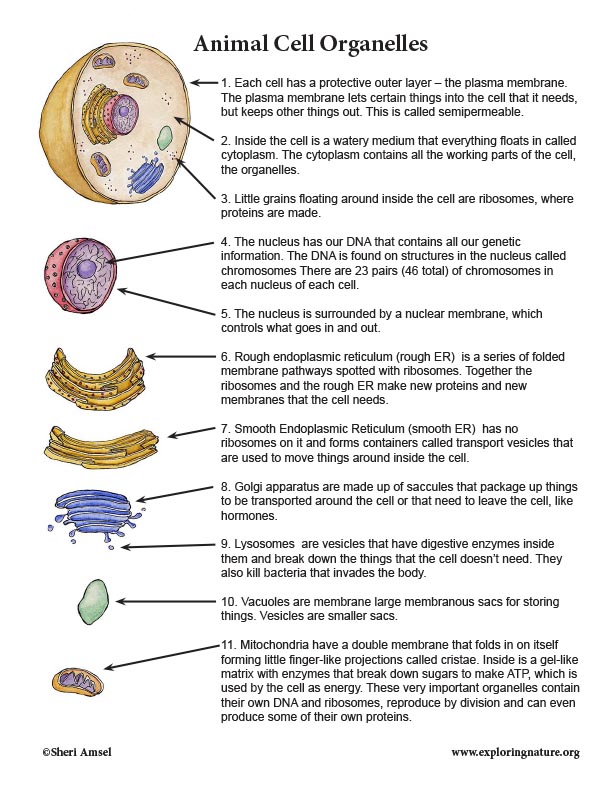
1. Each cell has a protective outer layer – the plasma membrane. The plasma membrane lets certain things into the cell that it needs, but keeps other things out. This is called semipermeable.
2. Inside the cell is a watery medium that everything floats in called cytoplasm. The cytoplasm contains all the working parts of the cell, the organelles.
3. Little grains floating around inside the cell are ribosomes, where proteins are made.
4. The nucleus has our DNA that contains all our genetic information. The DNA is found on structures in the nucleus called chromosomes There are 23 pairs (46 total) of chromosomes in each nucleus of each cell.
5. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane, which controls what goes in and out.
6. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) is a series of folded membrane pathways spotted with ribosomes. Together the ribosomes and the rough ER make new proteins and new membranes that the cell needs.
7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (smooth ER) has no ribosomes on it and forms containers called transport vesicles that are used to move things around inside the cell.
8. Golgi apparatus are made up of saccules that package up things to be transported around the cell or that need to leave the cell, like hormones.
9. Lysosomes are vesicles that have digestive enzymes inside them and break down the things that the cell doesn't need. They also kill bacteria that invades the body.
10. Vacuoles are membrane large membranous sacs for storing things. Vesicles are smaller sacs.
11. Mitochondria have a double membrane that folds in on itself forming little finger-like projections called cristae. Inside is a gel-like matrix with enzymes that break down sugars to make ATP, which is used by the cell as energy. These very important organelles contain their own DNA and ribosomes, reproduce by division and can even produce some of their own proteins.
Link to Short Answer Quiz to Assess Reading Comprehension for this Unit.
More Cell Resource Links:
Link to Color the Animal Cell
Link to Label the Animal Cell Organelles
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Cell Organelles" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/1043 >