To anyone who has lived by the ocean, the changing tide is as much a part of the day as sunrise and sunset – but why does the sea level change every day? The tides rise and fall because of the pull of gravity between the moon and Earth. Though this pull (or tractive force) is felt around the globe, nowhere is its effect more noticeable than on the free-moving water on the Earth’s surface. It is most noticeable on the ocean coastlines, but even large lakes experience tidal changes. The sun also pulls on the Earth, but it is so far away that its pull is less than half of the moon’s force. Luckily, Earth’s gravity keeps our oceans on the Earth, but the tug of war between the Earth and the moon results in our changing tides.
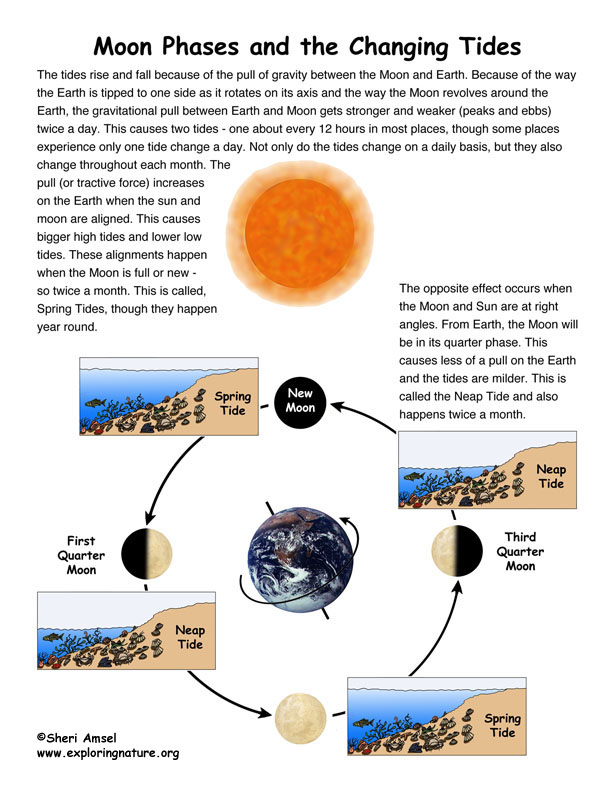
The gravitational pull between them gets higher and lower (peaks and ebbs) twice each day because of the way the Earth is tipped 23° to one side as it rotates on its axis – and as the moon revolves around it. This causes two tides - one about every 12 hours in most places. Some places experience only one tide change a day.
Tides do not happen at exactly the same time every day because the moon is not always in the same place and time daily – but a pattern does exist. The tidal patterns change by 50 minutes every day allowing us to chart the high and low tides throughout the year and watch for them.
Not only do the tides change on a daily basis, but they also change throughout each month. The pull (or tractive force) increases on the Earth when the sun and moon are aligned (in their positions as the Earth and moon revolve around the sun). This causes bigger high tides and lower low tides. These alignments happen when the moon is full or new - so twice a month. This is called, Spring Tides, though they happen year round.
The opposite effect occurs when the moon and sun are at right angles (in their positions as the Earth and moon revolve around the sun). From Earth, the moon will be in its quarter phase. This causes less of a pull on the Earth and the tides are milder. This is called the Neap Tide and also happens twice a month.
The tides are also affected by storms, the shape of the coastline and other factors. As the water rises, it is called the flood tide. When the tide is highest, it is called the high tide. When the tide is falling it is called the ebb tide. When the tide is lowest, it is called the low tide. The most extreme tidal change is seen in the Bay of Fundy in Nova Scotia where the water can rise and fall more than 50 feet (15.24 meters) throughout the day.
Using this information (above) draw a model of the Earth (include its tilt), phases of the moon and the tide patterns. The illustrated model below can be used as a guide.
Then take the short answer quiz below to test your knowledge about tides.
To test tidal action with inquiry, try this offsite NASA.gov activity.
Moon Phases and the Changing Tides – Short Answer Quiz
The tides rise and fall because of the pull of ______________________________ between the moon and Earth.
Though this pull (or ____________________________ force) is felt around the globe, nowhere is its effect more noticeable than on the free-moving water on the Earth’s surface.
The sun also pulls on the Earth, but it is so far away that its pull is less than half of the moon’s force. Luckily, Earth’s gravity keeps our oceans on the Earth, but the tug of war between the Earth and the moon results in our changing tides.
The gravitational pull between them gets higher and lower (peaks and ebbs) twice each day because of the way the Earth is tipped ___________ to one side as it rotates on its axis – and as the moon revolves around it.
This causes two tides - one about every ____________ hours in most places. Not only do the tides change on a daily basis, but they also change throughout each month.
The pull _________________________________ on the Earth when the sun and moon are aligned. This causes bigger high tides and lower low tides.
These alignments happen when the moon is _____________ or new - so twice a month.
This is called, __________________ Tides, though they happen year round. The opposite effect occurs when the moon and sun are at right angles. From Earth, the moon will be in its quarter phase.
This causes less of a pull on the Earth and the tides are milder. This is called the ___________________ Tide and also happens twice a month. The tides are also affected by storms, the shape of the coastline and other factors.
As the water rises, it is called the _________________ tide. When the tide is highest, it is called the __________________ tide.
When the tide is falling it is called the _________ tide.
When the tide is lowest, it is called the ____________ tide.
The most extreme tidal change is seen in the Bay of Fundy in Nova Scotia where the water can rise and fall more than 50 feet (15.24 meters) throughout the day.
(To print out for classroom use, see the PDF below.)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Tides and Phases of the Moon" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 14, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/1782 >