Bald eagles are found only in North America. They are more common in Alaska, Western Canada, the Northwest U. S., the upper Great Lakes, Florida and near Chesapeake Bay. But can be found here and there throughout the rest of the U.S.
They are found on big lakes, and along rivers and coastal areas where there is good fishing and tall trees for nesting.
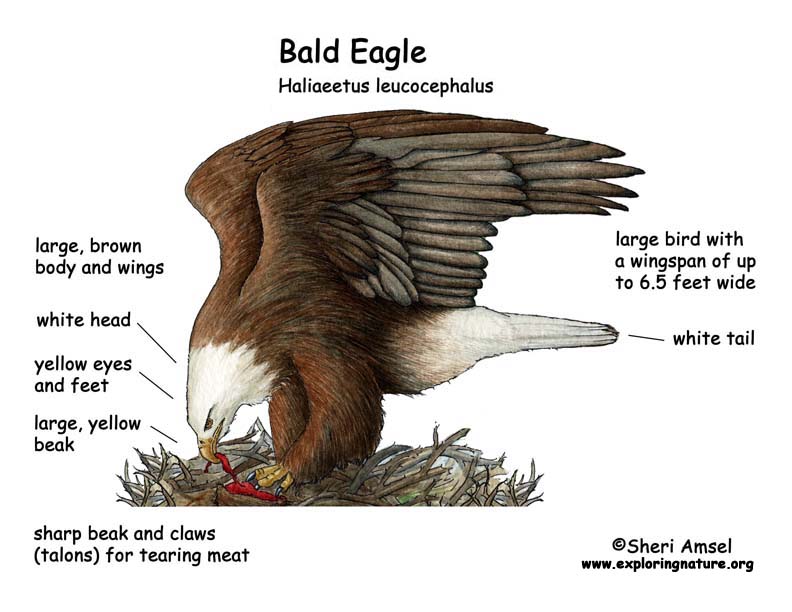
They are a very large bird with a wingspan (across open wings) of up to 6.5 feet! They have a white head and tail and a dark body, yellow eyes and feet and a large yellow beak. Their head and tail don’t turn white until they are almost 5 years old.
Bald eagles are sometimes called fish eagles because they eat mostly fish, if they can find it. They catch fish with their feet (talons) grabbing them right out of the water. They can live 30 years in the wild and longer in captivity.
They eat mostly fish, but will also hunt ducks, geese, and small mammals and will even eat dead animals (carrion).
Bald eagles find one mate for their whole lives (monogamous). They build a large nest, called an “aerie,” made of sticks, and branches in a large tree or up on a cliff. They may use the same nest every year, making it bigger and bigger over time. Nests that are 10 feet across have been seen. Females lay 2-3 eggs, in late fall to early spring (November – March). Both parents warm the eggs (incubate) for the month it takes them to hatch.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Aves
Order: Falconiformes
Family: Accipitridae
Genus: Haliaeetus
Species: H. leucocephalus
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Eagle (Bald)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 16, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/197 >