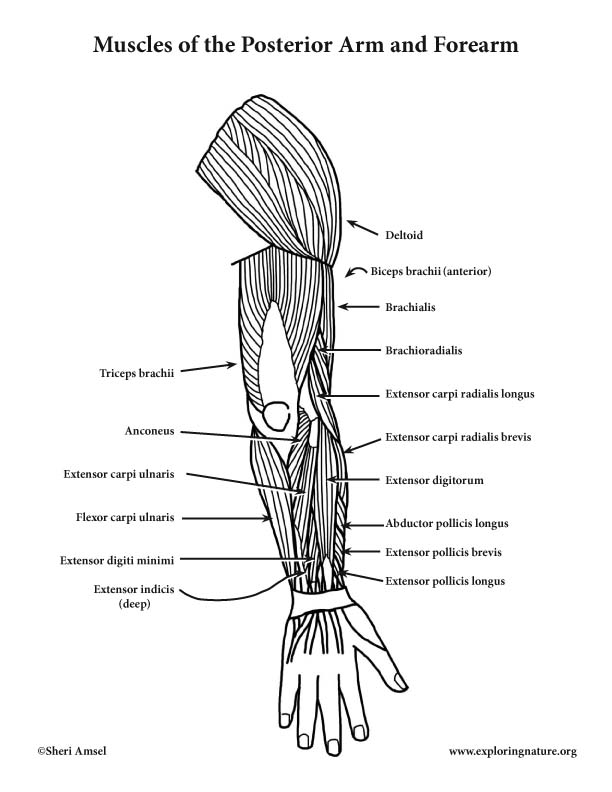
Muscles that Cross the Elbow (Moving the Forearm)
(posterior view)
1) Deltoid (Visible, but not part of this group as it moves arm from the shoulder only)
2) Triceps brachii
a. Actions: forearm extender, some adduction of arm
b. Innervation: Radial nerve
c. Origin: from posterior humerus and infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
d. Insertion: to olecranon process of the ulna
3) Anconeus
a. Actions: abducts the ulna when the arm is pronating (rotating forearm medially), helps triceps brachii extend forearm
b. Innervation: Radial nerve
c. Origin: from lateral epicondyle of the humerus
d. Insertion: to lateral olecranon process of ulna
Muscles that Cross the Elbow (Moving the Forearm)
(anterior – but viewed from the back)
4) Biceps brachii (NOT seen from the posterior)
a. Actions:: flexes and supinates forearm (supinate rotates forearm laterally) – these act together for pulling tissue from tissue box, also a minor arm flexor
b. Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve
c. Origin: from coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle on scapula
d. Insertion: through intertubercular groove of humerus to insert on radial tuberosity
5) Brachialis
a. Actions: flexes forearm
b. Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve
c. Origin: from anterior distal humerus
d. Insertion: to coronoid process of the ulna
6) Brachioradialis
a. Actions: flexes forearm (though doesn’t initiate flexion)
b. Innervation: Radial nerve
c. Origin: from distal humerus
d. Insertion: to styloid process of the radius
Muscles of the Forearm (Moving Wrist, Hand and Fingers)
(posterior compartment – Extensors)
l. Superficial Muscles
7) Flexor carpi ulnaris
a. Actions: flexes wrist, adducts hand
b. Innervation: Ulnar nerve
c. Origin: from medial epicondyle of the humerus and olecranon process of ulna
d. Insertion: to the base of the 5th metacarpal and pisiform bone (carpal).
8a) Extensor carpi radialis longus
a. Actions: extends wrist, abducts wrist
b. Innervation: Radial nerve
c. Origin: from lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
d. Insertion: to the base of the 2nd metacarpal
8b) Extensor carpi radialis brevis
a. Actions: extends wrist, abducts wrist (together with Extensor carpi radialis longus, it steadies the wrist when fingers are flexed)
b. Innervation: Radial nerve branch
c. Origin: from lateral epicondyle of the humerus
d. Insertion: to the base of the 3rd metacarpal
9) Extensor digitorum
a. Actions: extends wrist and fingers, abducts fingers (flares)
b. Innervation: Radial nerve branch
c. Origin: from lateral epicondyle of the humerus
d. Insertion:into four tendons of distal phalanges of fingers 2-5
10) Extensor carpi ulnaris
a. Actions: extends wrist, adducts wrist
b. Innervation: Radial nerve branch
c. Origin: from lateral epicondyle of humerus and posterior ulna
d. Insertion: to the base of the 5th metacarpal
ll. Deep Muscles
11) Supinator (NOT seen, deep to Extensor digitorum)
a. Actions: assists biceps to supinate forearm (laterally rotate from elbow)
b. Innervation: Radial nerve
c. Origin: from lateral epicondyle of humerus and proximal ulna
d. Insertion: to proximal radius
12) Abductor pollicis longus
a. Actions: abducts and extends thumb
b. Innervation: Radial nerve branch
c. Origin: from posterior radius and ulna
d. Insertion: to base of 1st metacarpal
13a) Extensor pollicis longus and brevis (13b)
a. Actions: extends thumb
b. Innervation: Radial nerve branch
c. Origin: from posterior radius and ulna
d. Insertion:to base of proximal and distal phalanx of thumb
14) Extensor Indicis (NOT seen, deep)
a. Actions: extends index finger
b. Innervation: Radial nerve branch
c. Origin: from posterior distal ulna
d. Insertion: to extensor expansion of index finger (where it joins Extensor digitorum)
15) Extensor digiti minimi
a. Actions: extends pinky (5th digit)
b. Innervation: Radial nerve branch
c. Origin: from lateral epicondyle of humerus
d. Insertion: to extensor expansion of pinky
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Use this study tool to learn the Muscles of the Posterior Arm and Forearm: Color the Muscles of the Arm and Forearm (Posterior)
Assess your knowlege of the Muscles of the Posterior Arm and Forearm: Label the Muscles of the Arm and Forearm (Posterior)
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________