Mississippi is a humid subtropical state with a history of rich forests, wetlands, coastal dunes, barrier islands and even some prairie.
Forest
Mississippi has almost 20 million acres of forest that covers 65% of the state. Pine forest makes up 33% of Mississippi's forests (6.62 million acres). Hardwood and oak pine forests together make up 53% of Mississippi's forest (10.5 million acres). Forest that is regrowing after fire, logging, development or other disturbances makes up the rest - 2.66% (a little more an 13 million acres). 77% of Mississippi's forests are privately owned.
Mississippi has lowland forests found in the floodplain of the Mississippi River that can tolerate "wet feet" during flood cycles. These forests were once rich with cypress, gum, hickory, oak, and cedar. Most were harvested in the last 100 years for lumber and converted into farm lands. Only 5-9% remain intact in places too wet to log or farm. These forests are important habitat for migrating birds.
Lowland forests can be broken down into different levels of flood tolerance. River swamp forests are found in areas that are flooded most of the time with trees that can survive extended time under water, like bald cypress, water tupelo and black willow. Lower hardwood swamp forests also tolerate some flooding, but still dry enough to allow more tree diversity with red maples, green ash, water hickory, and river birch. Backwater forests or Flats have all those trees plus other hardwoods like sycamore, oaks, and sweetgums. They also are thick with vines, creepers, and briers. Upland transitional forests are higher and only flood briefly each year so are more similar to mixed hardwood forests.
Wetlands
Before European settlers came to Mississippi, there were thought to be about 10 million acres of wetlands. After the first settlers arrived, wetlands were lost to farms. Then over time, wetlands were lost to roads, homes and businesses.
Wetlands are very important habitats. They provide valuable wildlife habitat, stabilize shorelines and protect the land from storm surges and flooding. They act as filters to pollutants that run off the land from farms, towns and cities. Despite this, wetlands have been drained and destroyed all over the U.S. until the late 1900s. Scientists think that as much as 50% of the wetlands in the U.S. are already gone. In Mississippi, wetland loss is estimated at about 60% – leaving about 4 million acres.
Mississippi has both freshwater and saltwater wetlands. It's freshwater wetlands (palustrine) include marshes, bogs, swamps, bottomland forests, bayheads, and coastal flatwoods. Mississippi's saltwater and brackish wetlands (estuarine) include coastal marshes, estuaries, mud flats and cypress-tupelo gum swamps.
For more information about Mississippi's natural habitats (off-site): LINK Another LINK
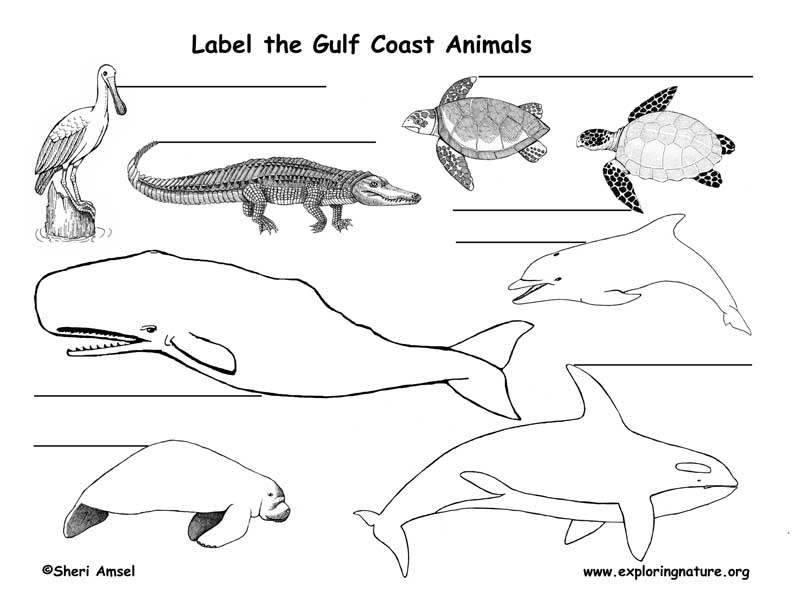
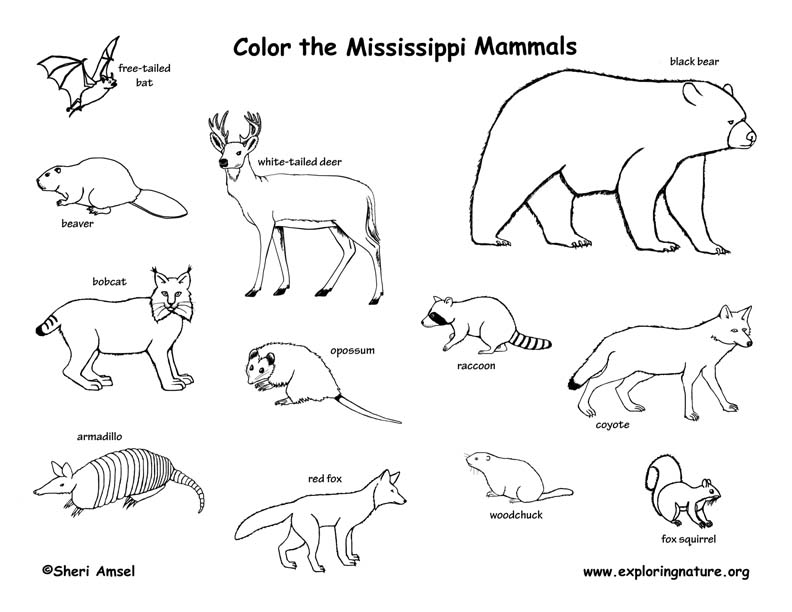
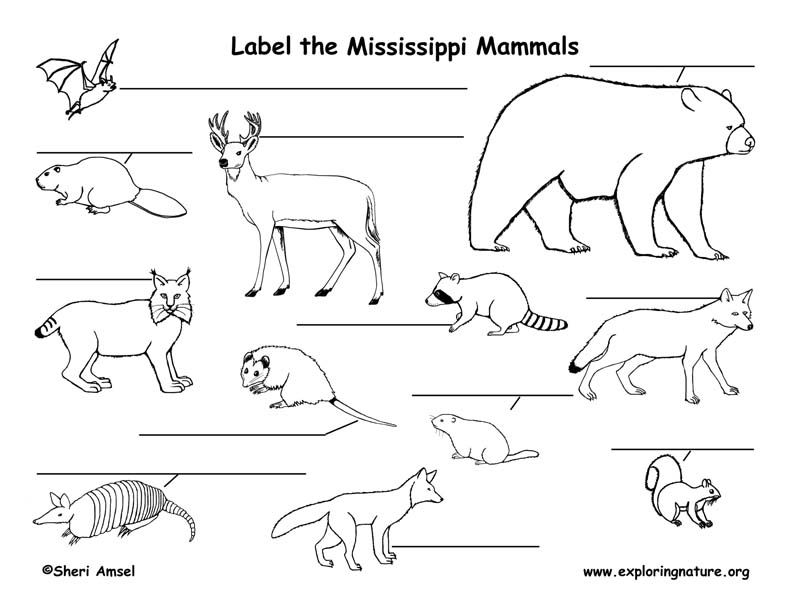
Gulf Mammals:
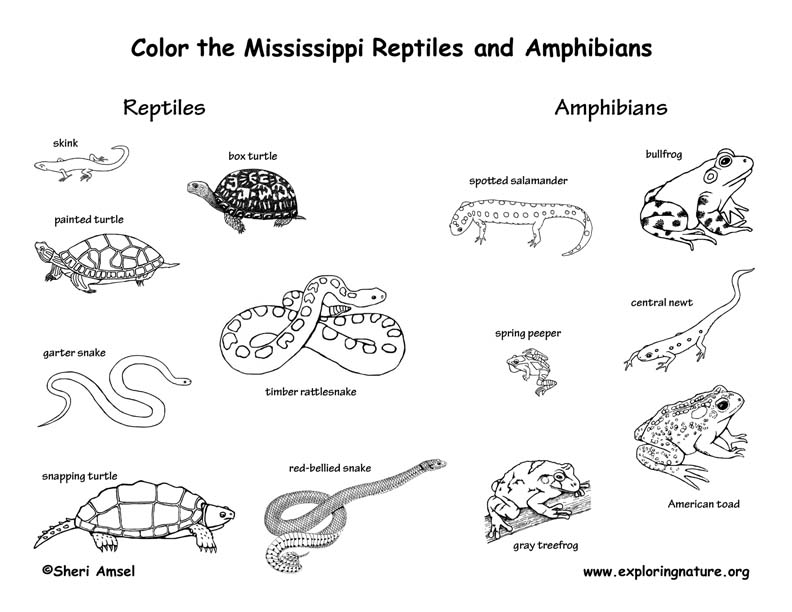
Amphibians:
Reptiles:
alligator (American)
anole (brown)
anole (northern green)
gecko (Mediterranean house)
lizard (eastern fence)
lizard (eastern glass)
lizard (eastern six-lined racerunner)
lizard (eastern slender glass)
lizard (mimic glass)
lizard (northern fence)
lizard (six-lined racerunner)
lizard (southern fence)
seaturtle (Atlantic hawksbill)
seaturtle (green)
seaturtle (Kemp's Ridley)
seaturtle (leatherback)
seaturtle (loggerhead)
skink (broad-headed)
skink (common five-lined)
skink (ground)
skink (little brown)
skink (northern coal)
skink (southern coal)
skink (southeastern five-lined)
snake (banded water)
snake (black-masked)
snake (black pine)
snake (black racer)
snake (broad-banded water)
snake (brown)
snake (brown water)
snake (canebrake rattlesnake)
snake (Carolina pygmy rattlesnake)
snake (coachwhip)
snake (common garter)
snake (common kingsnake)
snake (common rainbow)
snake (common ribbon)
snake (copperhead)
snake (coral)
snake (corn)
snake (cottonmouth)
snake (crayfish)
snake (DeKay's brown)
snake (Delta crayfish)
snake (dusky pygmy rattlesnake)
snake (eastern black)
snake (eastern chicken)
snake (eastern coachwhip)
snake (eastern copperhead)
snake (eastern coral)
snake (eastern corn)
snake (eastern cottonmouth)
snake (eastern diamondback rattlesnake)
snake (eastern garter)
snake (eastern hognose)
snake (eastern indigo)
snake (eastern king)
snake (eastern ribbon)
snake (eastern smooth)
snake (eastern worm)
snake (Florida red-bellied)
snake (glossy crayfish)
snake (gopher)
snake (Graham's crayfish)
snake (gray rat)
snake (Gulf coast ribbon)
snake (Gulf crayfish)
snake (Gulf salt marsh)
snake (harlequin coral)
snake (indigo)
snake (Louisiana milk)
snake (marsh brown)
snake (midland brown)
snake (midland water)
snake (midwestern worm)
snake (milk)
snake (Mississippi green water)
snake (Mississippi ring-necked)
snake (mole kingsnake)
snake (mud)
snake (northern diamond-backed water)
snake (northern pine)
snake (northern red-bellied)
snake (northern rough green)
snake (northern scarlet)
snake (northern water)
snake (orange-striped ribbon)
snake (pine woods littersnake)
snake (pine woods)
snake (plainbelly water)
snake (prairie kingsnake)
snake (pygmy rattlesnake)
snake (queen)
snake (racer)
snake (rainbow)
snake (rat)
snake (red-bellied)
snake (red milk)
snake (ringneck)
snake (rough earth)
snake (rough green)
snake (scarlet)
snake (scarlet king)
snake (smooth earth)
snake (southern black-masked)
snake (southern copperhead)
snake (southern hognose)
snake (southern water)
snake (southeastern crowned)
snake (speckled kingsnake)
snake (timber rattlesnake)
snake (western chicken)
snake (western cottonmouth)
snake (western diamondback rattlesnake)
snake (western pygmy rattlesnake)
snake (western mud)
snake (western smooth)
snake (yellow-bellied water)
terrapin (Mississippi diamondback)
tortoise (gopher)
turtle (Alabama map)
turtle (Alabama red-bellied cooter)
turtle (alligator snapping)
turtle (black-knobbed sawback)
turtle (common cooter)
turtle (common slider)
turtle (eastern box)
turtle (eastern chicken)
turtle (eastern mud)
turtle (eastern river cooter)
turtle (eastern snapping)
turtle (eastern spiny)
turtle (gopher tortoise)
turtle (Gulf Coast box)
turtle (Gulf Coast smooth softshell)
turtle (Gulf Coast spiny softshell)
turtle (Midland smooth softshell)
turtle (Mississippi diamond-backed terrapin)
turtle (Mississippi map)
turtle (Mississippi mud)
turtle (northern map)
turtle (Ouachita map)
turtle (Pascagoula map)
turtle (Pearl River map)
turtle (pond cooter)
turtle (razor-backed musk)
turtle (red-eared slider)
turtle (ringed sawback)
turtle (snapping)
turtle (southern painted)
turtle (stinkpot)
turtle (strip-necked musk)
turtle (three-toed box)
turtle (western chicken)
turtle (yellow-blotched sawback)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Mississippi Habitats, Mammals, Birds, Amphibians, Reptiles" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 14, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/833/ >