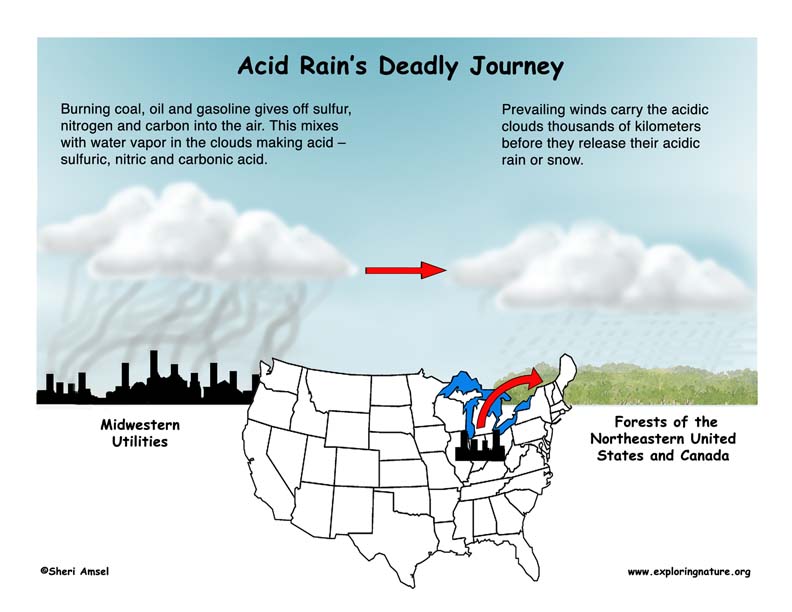
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ESS3.A: Natural Resources
• Energy and fuels that humans use are derived from natural sources, and their use affects the environment in multiple ways. Some resources are renewable over time, and others are not. (4-ESS3-1)
ESS3.B: Natural Hazards
• A variety of hazards result from natural processes (e.g., earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions). Humans cannot eliminate the hazards but can take steps to reduce their impacts. (4-ESS3-2) (Note: This Disciplinary Core Idea can also be found in 3.WC.)
ETS1.B: Designing Solutions to Engineering Problems
• Testing a solution involves investigating how well it performs under a range of likely conditions. (secondary to 4-ESS3-2)
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Use the Template and Resource Links to Fulfill NGSS
l. Goals:
Essential Questions:
NGSS Note: Think, question, entertain ideas.
ll. Introductory Activities to Assess Prior Knowledge
A. Simple Activities - that assess students’ understanding of natural hazards that are created by natural processes.
Understanding snowstorms:
Name the Storm Matching Activity
Understanding the Effects of Rainstorms:
Erosion Activity
Simple Activities - that assess students’ understanding of different kinds of natural resources.
A. Brainstorming Session
Question: What are some differemt kinds of natural resources and are they renewable?
lll. New Knowledge - Text
Read about natural hazards that can result from natural processes.
Endangered Species - The Giant Panda
Global Warming and Climate Change
Wetlands - Their Important and Why
Read about natural hazards that can result from natural processes.
Storms - Thunderstorms
Examples of Models (depicts the concept expressed in the reading):
Ask students to look at the models and explain how they illustrate the concepts in this unit.
Thunderstorm Model
V. Summarize Knowledge - Enduring Understandings
Vl. Next Generation of Science Standards (NGSS) - Grade 4
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ESS3.A: Natural Resources
• Energy and fuels that humans use are derived from natural sources, and their use affects the environment in multiple ways. Some resources are renewable over time, and others are not. (4-ESS3-1)
ESS3.B: Natural Hazards
• A variety of hazards result from natural processes (e.g., earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions). Humans cannot eliminate the hazards but can take steps to reduce their impacts. (4-ESS3-2) (Note: This Disciplinary Core Idea can also be found in 3.WC.)
ETS1.B: Designing Solutions to Engineering Problems
• Testing a solution involves investigating how well it performs under a range of likely conditions. (secondary to 4-ESS3-2)
Science and Engineering Practices
Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions
Constructing explanations and designing solutions in 3–5 builds on K–2 experiences and progresses to the use of evidence in constructing explanations that specify variables that describe and predict phenomena and in designing multiple solutions to design problems.
• Generate and compare multiple solutions to a problem based on how well they meet the criteria and constraints of the design solution. (4-ESS3-2)
Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Information
Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information in 3–5 builds on K–2 experiences and progresses to evaluate the merit and accuracy of ideas and methods.
• Obtain and combine information from books and other reliable media to explain phenomena. (4-ESS3-1)
Crosscutting Concepts
Cause and Effect
• Cause and effect relationships are routinely identified and used to explain change. (4-ESS3-1)
• Cause and effect relationships are routinely identified, tested, and used to explain change. (4-ESS3-2)
Connections to Engineering, Technology and Applications of Science
Interdependence of Science, Engineering, and Technology
• Knowledge of relevant scientific concepts and research findings is important in engineering. (4-ESS3-1)
Influence of Engineering, Technology, and Science on Society and the Natural World
• Over time, people’s needs and wants change, as do their demands for new and improved technologies. (4-ESS3-1)
• Engineers improve existing technologies or develop new ones to increase their benefits, to decrease known risks, and to meet societal demands. (4-ESS3-2)
Performance Expectations
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
4-ESS3-1. Obtain and combine information to describe that energy and fuels are derived from natural resources and their uses affect the environment. . [Clarification Statement: Examples of renewable energy resources could include wind energy, water behind dams, and sunlight; non-renewable energy resources are fossil fuels and fissile materials. Examples of environmental effects could include loss of habitat due to dams, loss of habitat due to surface mining, and air pollution from burning of fossil fuels.]
4-ESS3-2. Generate and compare multiple solutions to reduce the impacts of natural Earth processes on humans.* [Clarification Statement: Examples of solutions could include designing an earthquake resistant building and improving monitoring of volcanic activity.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to earthquakes, floods, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.]
Common Core State Standards Connections:
ELA/Literacy
RI.4.1 Refer to details and examples in a text when explaining what the text says explicitly and when drawing inferences from the text. (4-ESS3-2)
RI.4.9 Integrate information from two texts on the same topic in order to write or speak about the subject knowledgeably. (4-ESS3-2)
W.4.7 Conduct short research projects that build knowledge through investigation of different aspects of a topic. (4-ESS3-1)
W.4.8 Recall relevant information from experiences or gather relevant information from print and digital sources; take notes and categorize information, and provide a list of sources. (4-ESS3-1)
W.4.9 Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. (4-ESS3-1)
Mathematics
MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (4-ESS3-1),(4-ESS3-2)
MP.4 Model with mathematics. (4-ESS3-1),(4-ESS3-2)
4.OA.A.1 Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 × 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and 7 times as many as 5. Represent verbal statements of multiplicative comparisons as multiplication equations. (4-ESS3-1),(4-ESS3-2)
Connections to other DCIs in fourth grade:
4.EST1.C (4-ESS3-2)
Articulation of DCIs across grade-levels:
K.ETS1.A (4-ESS3-2); 2.ETS1.B (4-ESS3-2); 2.ETS1.C (4-ESS3-2); 5.ESS3.C (4-ESS3-1); MS.PS3.D (4-ESS3-1); MS.ESS2.A (4-ESS3-1),(4-ESS3-2); MS.ESS3.A (4-ESS3-1); MS.ESS3.B (4-ESS3-2); MS.ESS3.C (4-ESS3-1); MS.ESS3.D (4-ESS3-1); MS.ETS1.B (4-ESS3-2)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Grade 4 - 4-ESS3 Earth and Human Activity" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Grade-4-4-ESS3-Earth-and-Human-Activity >