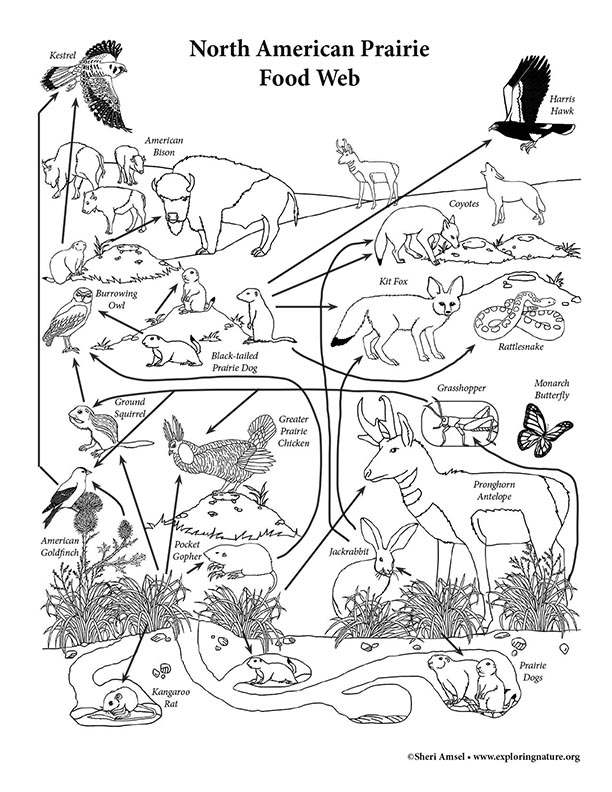
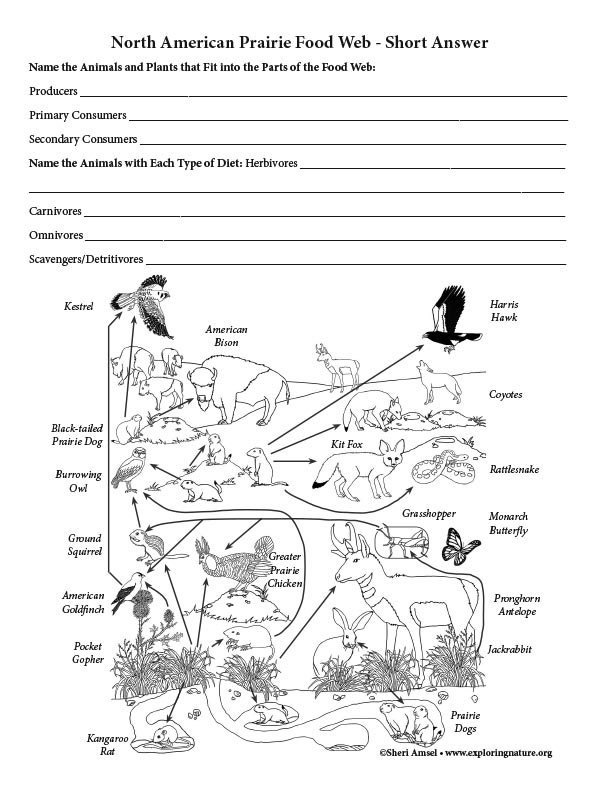
To understand the North American Prairie Food Web, first read about the North American Prairie using this link. Then read about the different trophic levels of a typical Food Chain (below). The trophic level is the position that an organism (plant or animal) occupies in a food chain - what it eats, and what eats it.
Energy flows through an ecosystem as one animal eats another animal or plant. Plants make (produce) their own food using water, sunlight and carbon dioxide (photosynthesis). Plants start the food chain. There are more plants than any other living thing because they are the bottom of the food chain. They provide the energy for everything else. They are the PRODUCERS.
The animals (insects, ground squirrels, prairie dogs, jackrabbits, pronghorn antelope) that mostly eat plants are called the herbivores. There are fewer herbivores than there are plants because each herbivore needs a lot of plant matter to live. Herbivores feed directly on the producers. They are the PRIMARY CONSUMERS.
Animals (rattlesnakes, kit foxes, hawks, coyotes) who eat the primary consumers (herbivores) are the SECONDARY CONSUMERS. They are carnivores. There are fewer secondary consumers than there are primary consumers because each secondary consumer needs to eat a lot of primary consumers to live.
Because there are fewer animals as you move up the food chain, it is really a food pyramid with the big carnivores needing to eat the most and so being the rarest of the animal kingdom. Because animals eat so many things, the food chain has many overlapping parts, so is really a FOOD WEB.
Last but not least, the DECOMPOSERS and DETRITIVORES eat and so recycle dead animals and plants (mushrooms, fungi, insects, bacteria). Detritivores can include the scavengers too. Nothing is wasted in a food web.
Print and fill out the North American Prairie Food Web - Short Answer Activity Sheet (pdf below).
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "North American Prairie Food Web Activity" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/North-American-Prairie-Food-Web-Activity >