They are found in the Northern Pacific, Indian, Northern Atlantic Oceans, and Mediterranean Sea during most of the year, then migrate to warm tropical waters to breed in the summer months.
They live out in upper layers of the open ocean (pelagic), but can be found as deep as 1,800 feet (600m).
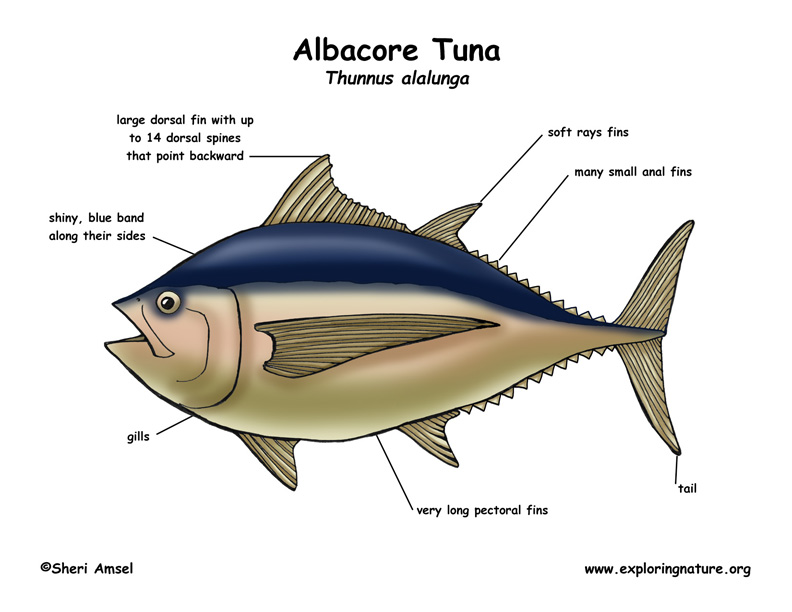
They can reach up to 4.5 feet long (140 cm) and weigh up to 130 pound (60 kg). They have very long pectoral fins as much as half their body length with a pointed tip. They have a large dorsal fin with up to 14 dorsal spines that point backward. This is followed down the back by many soft rays and small anal fins, all having a yellow color. They are covered in small scales and have a shiny, blue band along their sides.
They travel in large schools migrating throughout the year traveling to warmer waters to spawn and colder waters to feed. They often migrate with other kinds of tuna, like yellow and bluefin tunas and like to group around floating masses of seaweed.
They eat mostly small fish like skippers and anchovies, but will also eat squid and small ocean animals like shrimp and crabs when they find them.
They are eaten by sharks, but by far humans are their most dangerous prey.
They migrate to warm tropical waters in the summer months to spawn as a school, all releasing their eggs and sperm into the water at the same time. One female albacore tuna can release up to 3 million eggs a year. They do not care for their young.
They can live up to 13 years in good conditions. Due to heavy fishing by many countries worldwide, they are listed as vulnerable by the IUCN.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Actinopterygii
Order: Perciformes
Family: Scombridae
Genus: Thunnus
Species: T. alalunga
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Tuna (Albacore)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Tuna-Albacore >