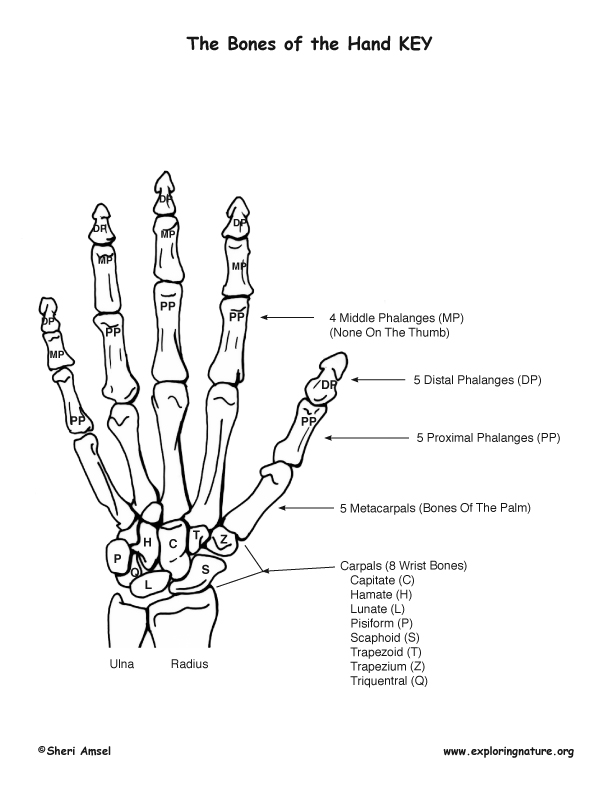
The hand includes the:
• carpals (wrist),
• metacarpals (palm)
• phalanges (fingers and thumb).
The hand has 27 bones; 8 carpels in the wrist, 5 metacarpels in the palm and 14 phalanges (each finger has 3, except the thumb, which has 2.)
The hand, with its many joints, is made to be flexible and agile. It can grasp and lift a heavy suitcase or carefully pick up a pin. The upper limb is made to do both.
LS1.A: Structure and Function
• All living things are made up of cells, which is the smallest unit that can be said to be alive. An organism may consist of one single cell (unicellular) or many different numbers and types of cells (multicellular). (MS-LS1-1)
• Within cells, special structures are responsible for particular functions, and the cell membrane forms the boundary that controls what enters and leaves the cell. (MS-LS1-2)
• In multicellular organisms, the body is a system of multiple interacting subsystems. These subsystems are groups of cells that work together to form tissues and organs that are specialized for particular body functions. (MS-LS1-3)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Hand - Bony Features" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 16, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/1065 >