Range and Habitat: They are all aquatic and mostly found in shallow coastal waters, though some are found in freshwater locations.
Physical Traits (Anatomy): They have 2 different body forms. Some species have both forms, but one form is always dominant.
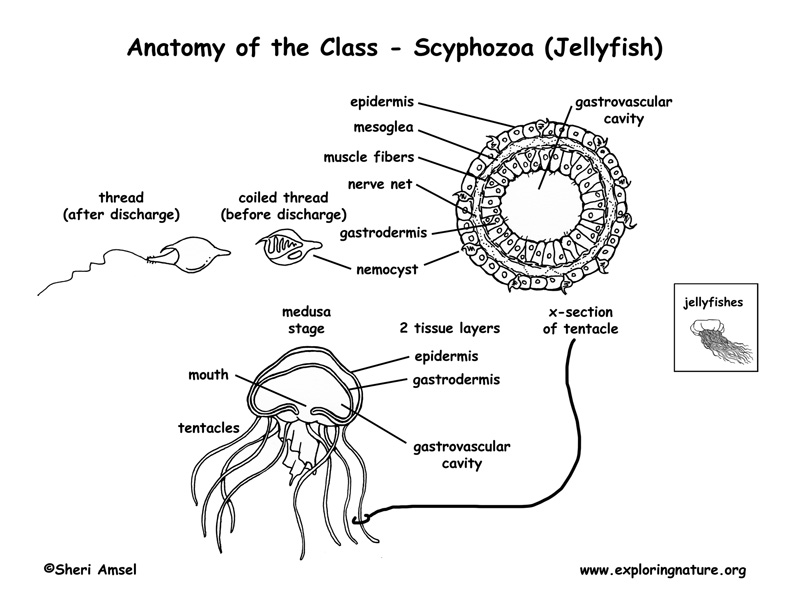
The “bell-shaped” form has the mouth facing downward and the animal contracts the bell to swim. The tentacles hang down and surround the mouth for pulling prey inside into the gastrovascular cavity for digestion. This body form is dominant in the adult true jellyfish, though they pass through a polyp phase as young.
The “polyp” form is usually anchored (sessile) with the mouth facing upward. Structurally, it is made up of a basal disc that attaches to the seabed and a cylindrical body stalk. Inside the body is the gastrovascular cavity. The mouth opens upward and is surrounded by tentacles. This is the dominant body form of the hydras, sea anemones and the corals. The Portuguese man-of-war is actually a gas-filled polyp that floats on the surface of the ocean trailing stinging polyps.
They have two cell layers – an outer protective epidermis and an inner gastrodermis. Between them is a jelly-like matrix called mesoglea. These layers surround an inner cavity called the gastrovascular cavity.
The epidermis layer is made up of many different types of cells. There are cells that contain muscles fibers (epitheliomuscular cells). These contract to allow the animal to move. Nerve cells make up a “nerve net” in the body that works with the muscle fibers to produce movement. There are also undifferentiated cells, called interstitial cells, that give rise to other cell types. Interstitial cells form eggs and sperm.
Interstitial cells also form cnidocytes in some species (like the jellyfish) which are special fluid-filled cells called “stinging cells.” Inside each stinging cell sits a spiral fiber, called a nematocyst, that is coiled and ready to spring. If a stinging cell is touched, it triggers the nematocyst, which instantly uncoils to catch prey. Some also inject a toxin that paralyzes prey. Then the tentacles around the mouth move the prey inside where it is digested. In some species, the cnidocyte cells contain spirocysts that are sticky threads that are used to catch prey or stick to surfaces. These are common in corals and sea anemones. There are also ptychocysts cells in some species, which help the animal anchor to the seabed.
The inner gastrodermis layer makes and secretes digestive fluids into the gastrovascular cavity where food is broken down and digested.
Habits (Behavior): When threatened, they will use their stinging cells to repel predators.
Diet: They are carnivores capturing prey as it drifts through their tentacles. Any contact triggers the discharge of stinging nematocysts that paralyze the prey. Then the tentacles will pull prey into the mouth and gastrovascular cavity. Once in the gastrovascular cavity, the gastrodermis cells secrete the digestive enzyme that breaks down the food. Waste is then ejected through the mouth with a sharp contraction of the body.
Reproduction: The reproductive process varies between the different cnidarians. In the class Scyphozoa (jellyfish) the fertilized gametes produce free-swimming larvae that swim away from the parent and embed on the sea floor. Here they grow into polyps. Each polyp can bud into a whole colony, which then releases the tiny medusa form that grows into an adult jellyfish.
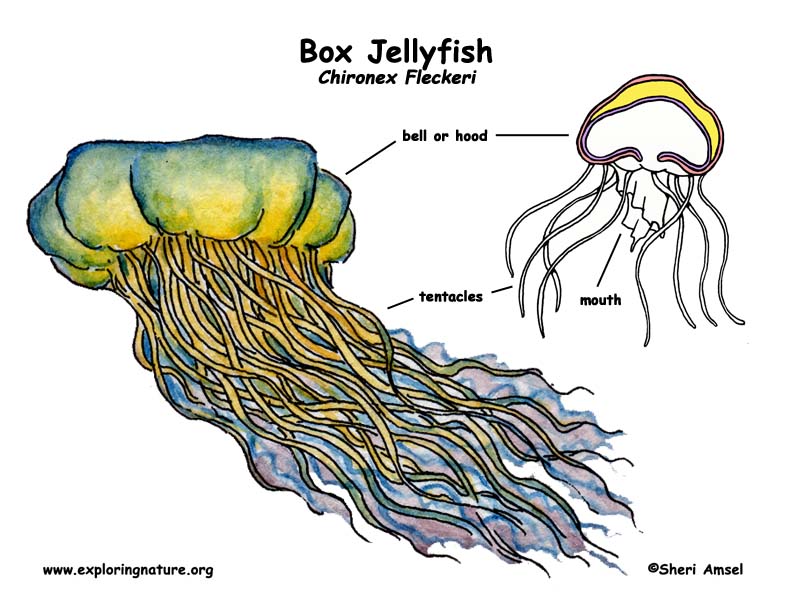
They are found in Northern Australian and Indo-Pacific region near the shore in shallow waters.
They are pale blue and see though. They are shaped like a bell or box shaped. They have up to 15 ten-foot-long tentacles on each corner, Each tentacle is covered with deadly stinging cells.
They move quickly through the water with a jet-like motion. Their sting is painful and deadly. This is so prey that happens into their tentacles dies quickly without tearing up the jellyfish. They are often at beaches where humans swim. Their sting will kill a human. They are the most deadly jellyfish in the world.
They eat shrimp and small fish.
Jellyfish lay eggs at the opening of a river in late summer. The eggs stick to rocks. In spring, the small jellyfish go back out to sea.
______________________________________________________________________________________
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Class - Scyphozoa (Jellyfish)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/1093 >