_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ESS3.A: Natural Resources
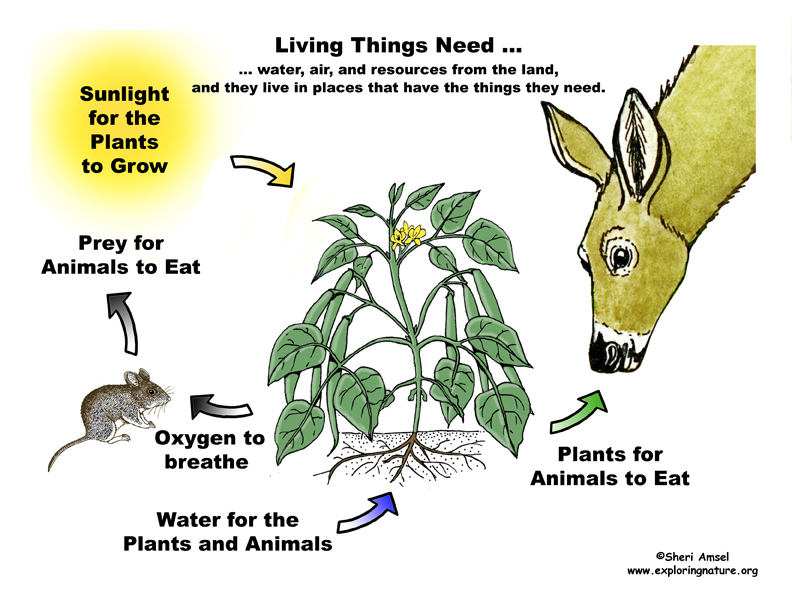
• Living things need water, air, and resources from the land, and they live in places that have the things they need. Humans use natural resources for everything they do. (K-ESS3-1)
ESS3.B: Natural Hazards
• Some kinds of severe weather are more likely than others in a given region. Weather scientists forecast severe weather so that the communities can prepare for and respond to these events. (K-ESS3-2)
ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
• Things that people do to live comfortably can affect the world around them. But they can make choices that reduce their impacts on the land, water, air, and other living things. (K-ESS3-3)
ETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting an Engineering Problem
• Asking questions, making observations, and gathering information are helpful in thinking about problems. (secondary to K-ESS3-2)
ETS1.B: Developing Possible Solutions
• Designs can be conveyed through sketches, drawings, or physical models. These representations are useful in communicating ideas for a problem’s solutions to other people. (secondary to K-ESS3-3)
Performance Expectations Students who demonstrate understanding can:
K-ESS3-1. Use a model to represent the relationship between the needs of different plants and animals (including humans) and the places they live. [Clarification Statement: Examples of relationships could include that deer eat buds and leaves, therefore, they usually live in forested areas; and, grasses need sunlight so they often grow in meadows. Plants, animals, and their surroundings make up a system.]
K-ESS3-2. Ask questions to obtain information about the purpose of weather forecasting to prepare for, and respond to, severe weather.* [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on local forms of severe weather.]
K-ESS3-3. Communicate solutions that will reduce the impact of humans on the land, water, air, and/or other living things in the local environment.* [Clarification Statement: Examples of human impact on the land could include cutting trees to produce paper and using resources to produce bottles. Examples of solutions could include reusing paper and recycling cans and bottles.]
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Use the Template and Resource Links to Fulfill NGSS
l. Goals:
Essential Questions:
NGSS Note: Think, question, entertain ideas.
ll. Introductory Activities to Assess Prior Knowledge
ESS3.A: Natural Resources
A. Simple Activities - that assess students’ understanding of what animal need to survive in their habitats.
What Do Living Things Need? Fill in The Blank
What Do Living Things Need - Matching
What Living Things Need - Labeling
ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
How Do Humans Affect Their Environment? Critical Thinking
ESS3.B: Natural Hazards
A. Read to your students about weather and environmental issues:
Seasonal Posters - Winter, Spring, Summer, Fall
ESS3.B: Natural Hazards
ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
Human Impacts on Earth Systems - Poster
Humans Affect Earth Systems - Coloring Page
Environmental Issues
Global Warming and Climate Change
ESS3.A: Natural Resources
B. Familiarize students with what animals need to survive and how specific habitats suit their survival needs:
Animals in their Habitat - Model Making (K-1)
What Do Lions Eat? Foldable Activity
What Do Grizzly Bears Eat? Foldable Activity
What Do Polar Bears Eat? Foldable Activity
Natural Resources - Read Aloud
Natural Resources - Comparing Turtles Mini-Poster
Natural Resources - Vocabulary Cut and Paste
Natural Resources for Turtles - Matching
What Natural Resources Living Things Need - Matching
Habitats and the Natural Resource Needs of Animals - Matching
Natural Resources Living Things Need - Cut & Paste
Ocean Natural Resources - Matching
Rainforest Natural Resources - Matching
Desert Natural Resources - Matching
Examples of Models (depicts the concept expressed in the reading):
Ask students to look at the models of what animals need, weather phenomenon and environmental issues and explain how each illustrates the concepts in this standard.
Which Resources Do YOU Use - Critical Thinking
Inquiry related to human over-use and destruction of Earth's resources:
Smog-making Activity
Use critical thinking to devise ways to protect people from natural hazards. Read about wetlands and how they protect us from natural processes (storms) that produce natural hazards (flooding). Knowing this, what actions do you think we should take to help protect us from storm flooding?
Wetlands - Their Important and Why
Human Actions: Sometimes human actions combine with natural processes to create new natural hazards. Read about acid rain and its effect on us. Use critical thinking about ways we can reduce this hazard.
V. Summarize Knowledge - Enduring Understandings
Vl. Next Generation of Science Standards (NGSS) - Kindergarten
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ESS3.A: Natural Resources
• Living things need water, air, and resources from the land, and they live in places that have the things they need. Humans use natural resources for everything they do. (K-ESS3-1)
ESS3.B: Natural Hazards
• Some kinds of severe weather are more likely than others in a given region. Weather scientists forecast severe weather so that the communities can prepare for and respond to these events. (K-ESS3-2)
ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
• Things that people do to live comfortably can affect the world around them. But they can make choices that reduce their impacts on the land, water, air, and other living things. (K-ESS3-3)
ETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting an Engineering Problem
• Asking questions, making observations, and gathering information are helpful in thinking about problems. (secondary to K-ESS3-2)
ETS1.B: Developing Possible Solutions
• Designs can be conveyed through sketches, drawings, or physical models. These representations are useful in communicating ideas for a problem’s solutions to other people. (secondary to K-ESS3-3)
Science and Engineering Practices
Asking Questions and Defining Problems
Asking questions and defining problems in grades K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to simple descriptive questions that can be tested.
• Ask questions based on observations to find more information about the designed world. (K-ESS3-2)
Developing and Using Models
Analyzing Modeling in K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to include using and developing models (i.e., diagram, drawing, physical replica, diorama, dramatization, storyboard) that represent concrete events or design solutions.
• Use a model to represent relationships in the natural world. (K-ESS3-1)
Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Information
Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information in K–2 builds on prior experiences and uses observations and texts to communicate new information.
• Read grade-appropriate texts and/or use media to obtain scientific information to describe patterns in the natural world. (K-ESS3-2)
• Communicate solutions with others in oral and/or written forms using models and/or drawings that provide detail about scientific ideas. (K-ESS3-3)
Crosscutting Concepts
Cause and Effect
• Events have causes that generate observable patterns. (K-ESS3-2),(K-ESS3-3)
Systems and System Models
• Systems in the natural and designed world have parts that work together. (K-ESS3-1)
Connections to Engineering, Technology and Applications of Science
Interdependence of Science, Engineering, and Technology
• People encounter questions about the natural world every day. (K-ESS3-2)
Influence of Science, Engineering, and Technology on Society and the Natural World
• People depend on various technologies in their lives; human life would be very different without technology. (K-ESS3-2)
Performance Expectations
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
K-ESS3-1. Use a model to represent the relationship between the needs of different plants and animals (including humans) and the places they live. [Clarification Statement: Examples of relationships could include that deer eat buds and leaves, therefore, they usually live in forested areas; and, grasses need sunlight so they often grow in meadows. Plants, animals, and their surroundings make up a system.]
K-ESS3-2. Ask questions to obtain information about the purpose of weather forecasting to prepare for, and respond to, severe weather.* [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on local forms of severe weather.]
K-ESS3-3. Communicate solutions that will reduce the impact of humans on the land, water, air, and/or other living things in the local environment.* [Clarification Statement: Examples of human impact on the land could include cutting trees to produce paper and using resources to produce bottles. Examples of solutions could include reusing paper and recycling cans and bottles.]
Common Core State Standards Connections:
RI.K.1 With prompting and support, ask and answer questions about key details in a text. (K-ESS3-2)
W.K.2 Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to compose informative/explanatory texts in which they name what they are writing about and supply some information about the topic. (K-ESS3-3)
SL.K.3 Ask and answer questions in order to seek help, get information, or clarify something that is not understood. (K-ESS3-2)
SL.K.5 Add drawings or other visual displays to descriptions as desired to provide additional detail. (K-ESS3-1)
Mathematics
MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (K-ESS3-1)
MP.4 Model with mathematics. (K-ESS3-1),(K-ESS3-2)
K.CC Counting and Cardinality (K-ESS3-1),(K-ESS3-2)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Kindergarten - K-ESS3 Earth and Human Activity" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 17, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/1977 >