They are found throughout North America.
They live in the leaf litter of the forest, under rocks, and in rotten logs. They are also found around the house and in barns, basements, and garages.
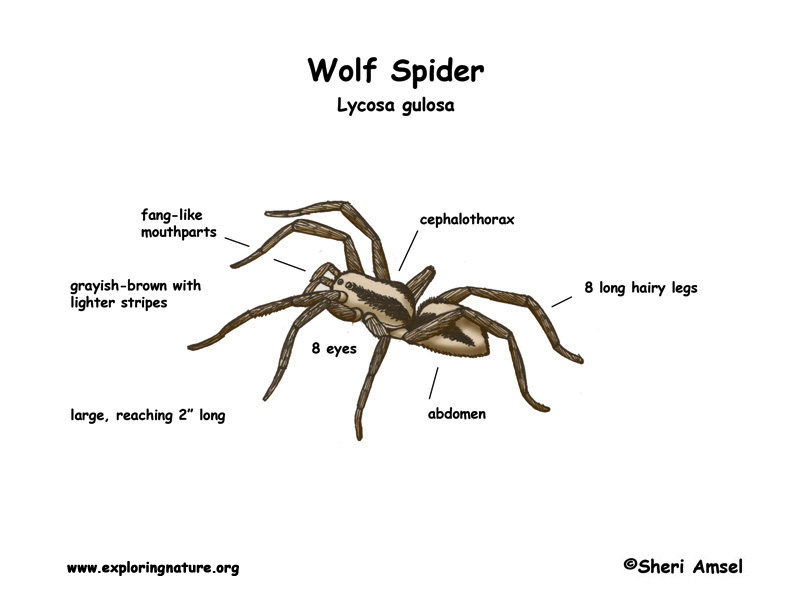
They can be large, reaching 2” long with long, hairy legs. They are grayish-brown with lighter stripes. This helps them blend into their habitat (camouflage). They have eight eyes arranged in rows. They have fang-like mouthparts called chelicerae.
They do not make a web. They travel around at night hunting insects to eat. They can run very quickly. They will bite, but they are not poisonous.
They eat insects and other spiders.
Females lay eggs into a light-colored, round, silken egg sac, which she carries around on her abdomen. When the babies (spiderlings) hatch out of the egg sac they crawl onto their mother’s back and stay there until they are big enough to survive on their own. They shed their skin several times before becoming an adult.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Arachnida
Order: Araneae
Superfamily: Lycosoidea
Family: Lycosidae
Genus: Lycosa
Species: L. gulosa
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Spider (Wolf) " Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 15, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/579 >